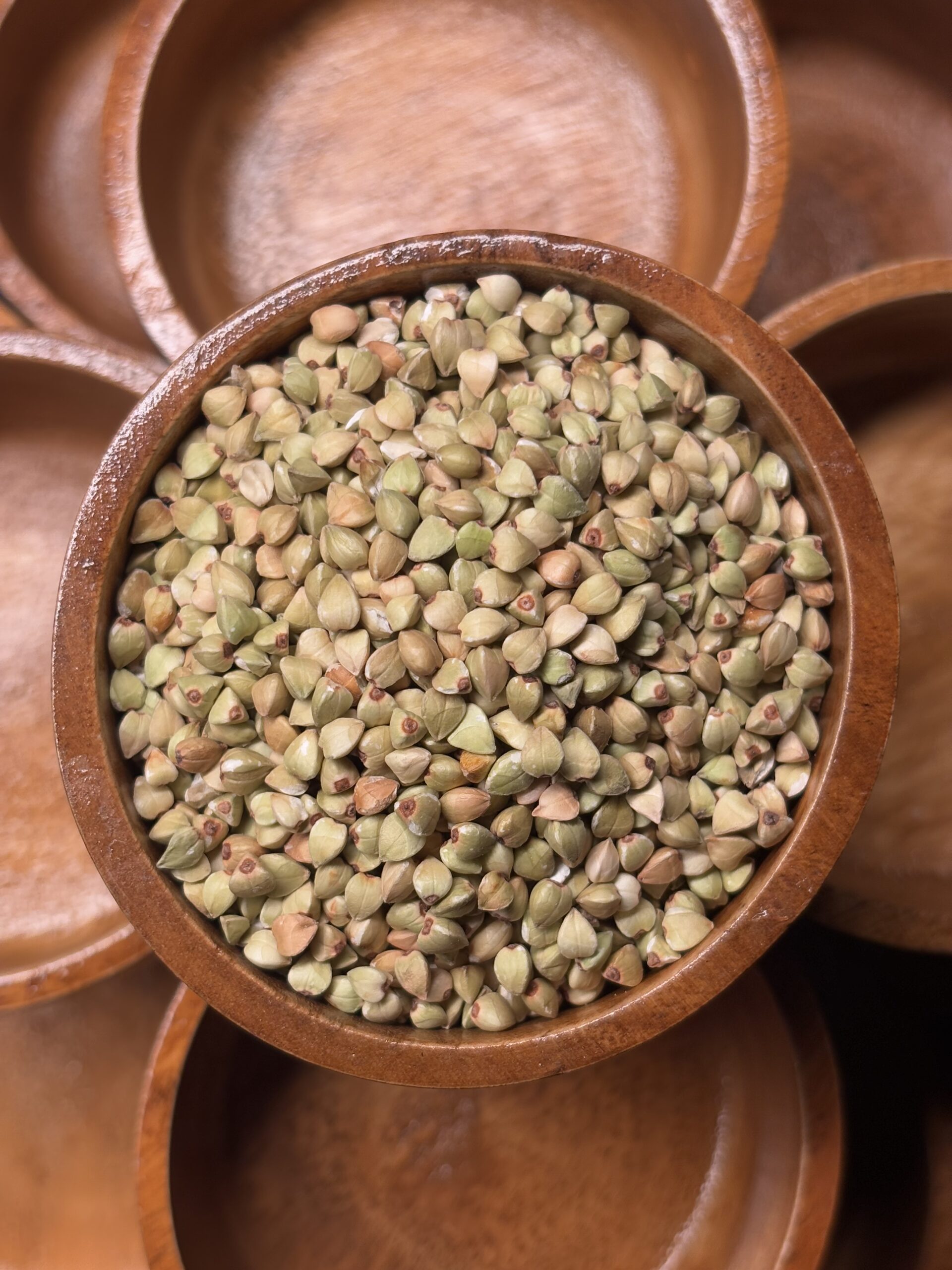
About Buckwheat
Buckwheat, a nutritious pseudograin, offers a good source of protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates, along with essential minerals and antioxidants, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Key Features:
- Buckwheat is a good source of protein, containing around 13.3 grams per 100 grams.
- It's rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber, contributing to digestive health.
- Buckwheat provides complex carbohydrates, which are slowly digested and help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- It contains essential minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and iron.
- Buckwheat is a source of B vitamins, including thiamine (B1) and riboflavin (B2).
- Buckwheat is rich in antioxidants, including rutin, which may offer various health benefits.
- Buckwheat is naturally gluten-free, making it suitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
- The complex carbohydrates and fiber in buckwheat can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Buckwheat may contribute to heart health due to its fiber content and antioxidant properties.
- The high fiber content supports healthy digestion and regular bowel movements.
- Buckwheat contains antioxidants that help protect against cell damage.
- Among many cereals and millets, Buckwheat is the richest source of protein content. Per 100 grams, the grain has a whopping 13.3 grams of protein.
- The amino acid profile of the buckwheat millet is notable for its high lysine, which is deficient in most cereals out there.
Nutritional Facts (per 100g)
| Calories | 343 kcal |
|---|
| Protein | 13.3 grams |
|---|
| Carbohydrates | 71.5 grams |
|---|
| Fiber | 10 grams |
|---|
| Fat | 3.4 grams |
|---|
| Magnesium | 86 mg |
|---|
| Phosphorus | 118 mg |
|---|
| Potassium | 148 mg |
|---|
| Calcium | 12 mg |
|---|
| Iron | 1.34 mg |
|---|