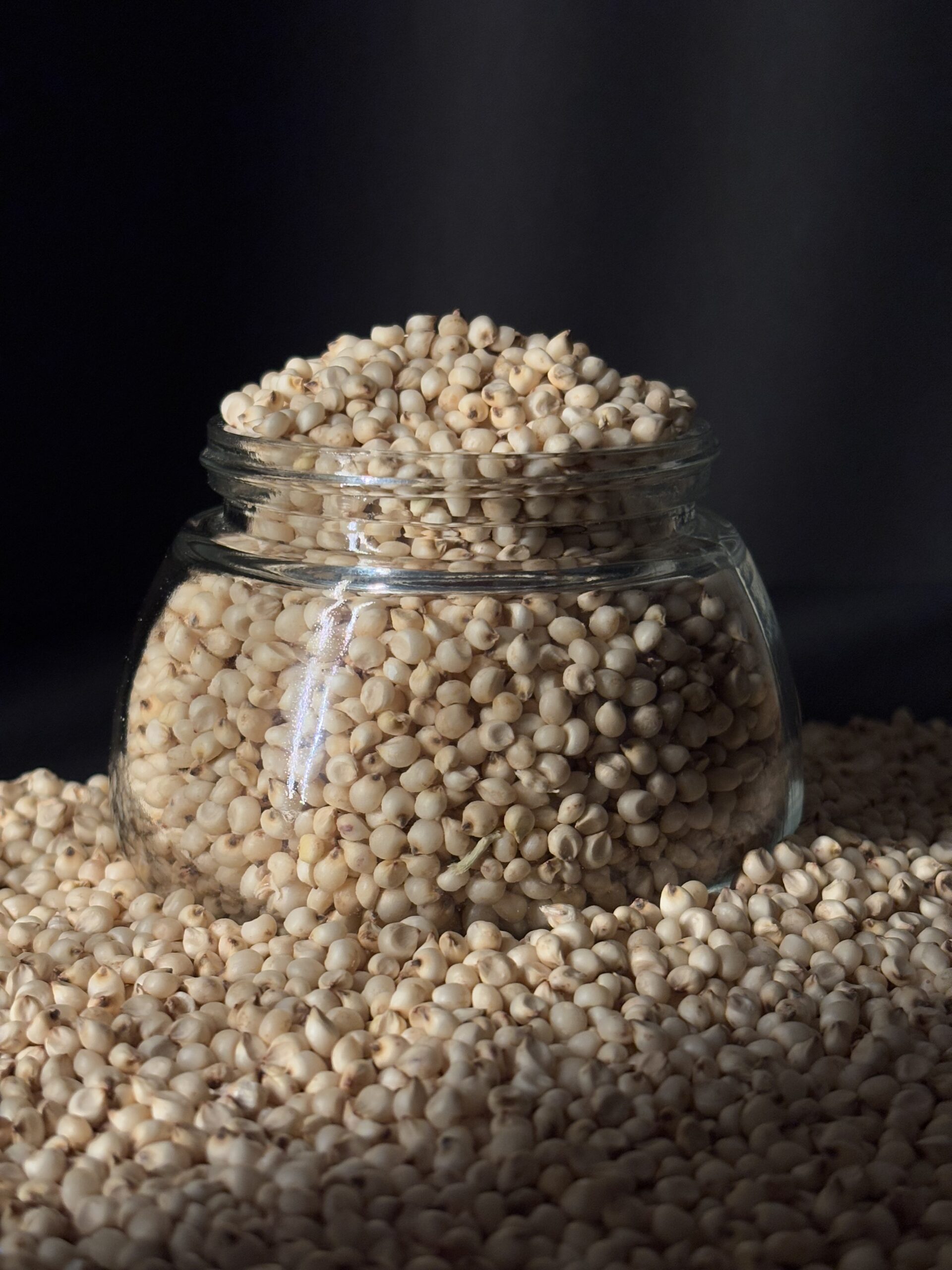
About Sorghum Millet (Jowar)
Sorghum, also known as jowar, is a versatile, gluten-free grain, a staple in many regions, especially in Africa and Asia, and is a good source of protein, fibre, and antioxidants, used in various food preparations and even for animal feed and biofuels.
- Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) is a grass species cultivated for its grain, also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo.
- Millets are a group of small-seeded cereal grains, with pearl millet being a prominent example.
- Sorghum and millets are important staple crops in semi-arid regions of Africa and Asia, providing essential nutrients for millions.
- Sorghum is the world's fifth most important cereal, and millets are the seventh most important.
- These crops are known for their resilience and ability to thrive in harsh environments with limited water and resources.
- Sorghum is a good source of protein, fiber, and essential minerals like calcium and iron.
- Sorghum is naturally gluten-free, making it a suitable option for people with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
- Sorghum can be used in various food preparations, including porridge, flatbreads, cakes, and alcoholic beverages.
- Sorghum is also used for animal feed, biofuel production, and industrial applications.
- Sorghum and millets have a long history of use in traditional food and beverage preparations in many cultures.
- Sorghum contains antioxidants that may help protect against cell damage.
- Sorghum has a low glycemic index, meaning it doesn't cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Sorghum may support heart health due to its fiber content and essential nutrients.
- Sorghum's low glycemic index and fiber content can be beneficial for managing blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
Nutritional Facts (per 100g)
| Energy | 1,380 kJ (330 kcal) |
|---|
| Carbohydrates | 72.1 g |
|---|
| Sugar | 2.53 g |
|---|
| Dietary Fiber | 6.7 g |
|---|
| Fat | 3.46 g |
|---|
| Saturated Fat | 0.61 g |
|---|
| Monounsaturated Fat | 1.13 g |
|---|
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.56 g |
|---|
| Protein | 10.6 g |
|---|
| Thiamine (B1) | 0.332 mg (28% DV) |
|---|
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0.096 mg (7% DV) |
|---|
| Niacin (B3) | 3.69 mg (23% DV) |
|---|
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | 0.367 mg (7% DV) |
|---|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.443 mg (26% DV) |
|---|
| Folate (B9) | 20 μg (5% DV) |
|---|
| Vitamin E | 0.5 mg (3% DV) |
|---|
| Calcium | 13 mg (1% DV) |
|---|
| Copper | 0.284 mg (32% DV) |
|---|
| Iron | 3.36 mg (19% DV) |
|---|
| Magnesium | 165 mg (39% DV) |
|---|
| Manganese | 1.6 mg (70% DV) |
|---|
| Phosphorus | 289 mg (23% DV) |
|---|
| Potassium | 363 mg (12% DV) |
|---|
| Selenium | 12.2 μg (22% DV) |
|---|
| Sodium | 2 mg (0% DV) |
|---|
| Zinc | 1.67 mg (15% DV) |
|---|